
Renewable Resources Utilization 2024
Renewable resources have emerged as a crucial aspect of sustainable development in the modern era. As the world faces pressing environmental challenges, the utilization of renewable resources offers a promising solution to meet energy needs while minimizing ecological harm. In this article, we delve into the various facets of renewable resource utilization, from its types and advantages to challenges, innovations, and global impact.
Introduction to Renewable Resources
Renewable resources encompass a wide range of natural energy sources that are replenished naturally over time. Unlike finite fossil fuels such as coal and oil, renewable resources are virtually inexhaustible and have minimal environmental impact during extraction and consumption. Examples include solar energy, wind power, hydroelectricity, biomass, and geothermal energy. These resources play a pivotal role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable development.
Types of Renewable Resources
Solar Energy
Solar energy harnesses the power of sunlight through photovoltaic cells or solar panels to generate electricity. It is abundant, clean, and renewable, making it an attractive option for both residential and commercial applications.
Wind Energy
Wind energy utilizes wind turbines to convert kinetic energy from the wind into electricity. Wind farms are increasingly common in regions with consistent wind patterns, providing a reliable source of renewable power.
Hydroelectric Power
Hydroelectric power involves the generation of electricity from flowing water, typically through the use of dams and turbines. It is one of the oldest and most widely used forms of renewable energy, accounting for a significant portion of global electricity production.
Biomass
Biomass refers to organic materials such as wood, crop residues, and waste that can be converted into energy through processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. Biomass energy is versatile and can be used for heating, electricity generation, and transportation fuels.
Geothermal Energy
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth’s interior to generate electricity or provide heating and cooling. It relies on geothermal reservoirs and technologies such as geothermal heat pumps and binary cycle power plants.
Advantages of Utilizing Renewable Resources
The utilization of renewable resources offers numerous benefits across environmental, economic, and social domains.
Environmental Benefits
Renewable energy sources produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions and pollutants compared to fossil fuels, helping mitigate climate change and air pollution. They also have lower environmental impact during extraction and production.
Economic Benefits
Investing in renewable energy creates jobs, stimulates economic growth, and reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, thereby enhancing energy security. Renewable resources can also provide long-term cost savings through reduced fuel and maintenance expenses.
Social Benefits
Renewable energy projects can contribute to community development by providing reliable electricity access, improving public health, and fostering energy independence. They also promote energy equity by decentralizing power generation and empowering local stakeholders.
Challenges in Utilizing Renewable Resources
Despite their many advantages, renewable resources face several challenges that hinder their widespread adoption.
Intermittency
Some renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, are intermittent and dependent on weather conditions. This intermittency can lead to fluctuations in energy output and requires effective storage and backup solutions.
Storage Issues
Storing energy from renewable sources for later use remains a significant challenge, particularly at scale. Advances in battery technologies and grid integration are needed to overcome storage limitations and ensure reliable energy supply.
Infrastructure Requirements
The transition to renewable energy requires substantial investments in infrastructure, including transmission lines, storage facilities, and grid modernization. Expanding and upgrading existing infrastructure is essential to accommodate renewable energy integration.
Initial Investment
While renewable energy technologies have become increasingly cost-competitive, the upfront capital costs can be prohibitive for some projects. Access to financing and supportive policies are critical to overcoming financial barriers and attracting investment.
Innovations in Renewable Resource Utilization
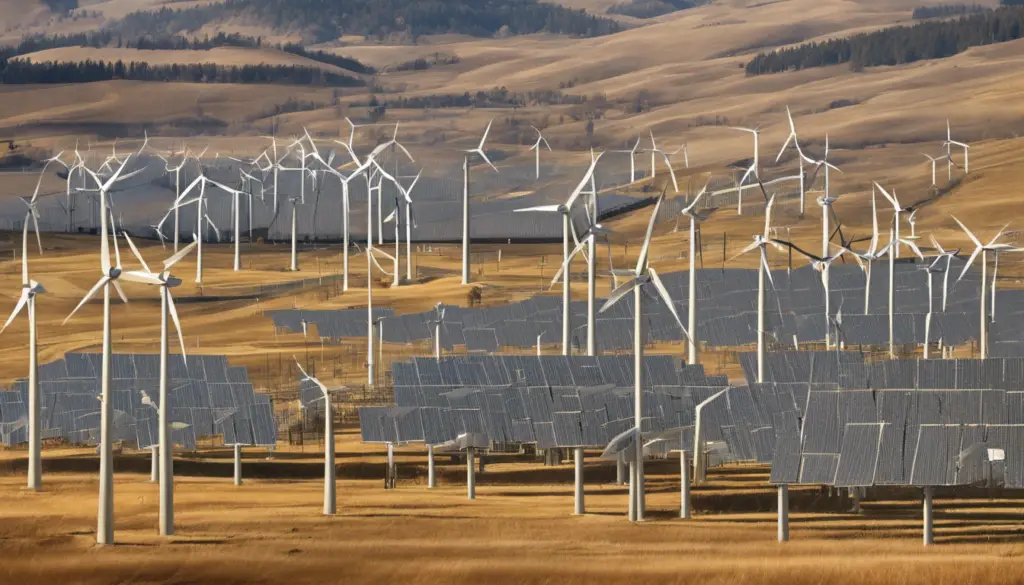

Technological advancements and innovation play a vital role in overcoming challenges and driving the growth of renewable resource utilization.
Technological Advancements
Advances in solar panel efficiency, wind turbine design, and energy storage technologies have made renewable energy more reliable and cost-effective. Continued research and development are essential to further improve performance and reduce costs.
Research and Development
Investments in research and development are essential for unlocking the full potential of renewable resources. Innovations in materials science, engineering, and energy conversion technologies can lead to breakthroughs in renewable energy generation, storage, and distribution.
Government Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting renewable resource utilization and overcoming market barriers.
Subsidies
Subsidies and financial incentives encourage investment in renewable energy projects by reducing costs and providing financial support. Subsidy programs may include tax credits, grants, feed-in tariffs, and renewable energy certificates.
Tax Credits
Tax incentives such as production tax credits and investment tax credits help offset the capital costs of renewable energy installations and encourage private sector investment. These credits can significantly improve project economics and accelerate deployment.
Renewable Energy Targets
Many governments have established renewable energy targets and mandates to increase the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix. These targets create market certainty and drive investment in renewable energy infrastructure.
Global Impact of Renewable Resource Utilization
The widespread adoption of renewable resources has far-reaching implications for global sustainability and development.
Mitigating Climate Change
By reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning away from fossil fuels, renewable resources play a crucial role in mitigating climate change and limiting global warming. They offer a pathway to a low-carbon future and help meet international climate targets.
Reducing Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Diversifying the energy mix with renewable resources reduces dependence on finite fossil fuels and enhances energy security. Renewable energy sources are indigenous and abundant, reducing reliance on imported oil and gas.
Sustainable Development
Renewable energy promotes sustainable development by providing clean, affordable, and accessible energy for all. It supports economic growth, reduces poverty, and improves health and well-being, particularly in developing countries.
Case Studies of Successful Renewable Resource Utilization Projects
Numerous successful renewable energy projects demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of renewable resource utilization.
Solar Farms
Large-scale solar farms, such as the Topaz Solar Farm in California and the Solar Energy Generating Systems in Nevada, demonstrate the potential of solar energy to generate electricity at utility scale.
Wind Turbines
Wind farms like the Alta Wind Energy Center in California and the Gansu Wind Farm in China showcase the capacity of wind energy to provide clean, renewable power to communities and industries.
Hydroelectric Dams
Hydroelectric projects such as the Three Gorges Dam in China and the Itaipu Dam on the Brazil-Paraguay border highlight the role of hydropower in meeting electricity demand and supporting economic development.
Biomass Power Plants
Biomass power plants like the Drax Power Station in the UK and the Mascoma Biomass Facility in New Hampshire illustrate the potential of biomass energy to generate electricity from organic waste and residues.
Future Prospects and Trends
The future of renewable resource utilization is promising, with continued growth and innovation expected in the coming years.
Growth Projections
Global renewable energy capacity is projected to continue expanding rapidly, driven by declining costs, supportive policies, and increasing demand for clean energy. Solar and wind power are expected to lead the way in terms of capacity additions.
Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies such as advanced energy storage, floating solar, and enhanced geothermal systems hold great potential for further enhancing the efficiency and scalability of renewable energy systems.
Market Opportunities
The transition to renewable energy presents significant market opportunities for businesses, investors, and innovators. Opportunities exist across the value chain, from project development and construction to manufacturing, operations, and maintenance.
Role of Businesses and Individuals
Businesses and individuals play a crucial role in advancing renewable resource utilization and driving the transition to a sustainable energy future.
Adopting Renewable Energy Practices
Businesses can reduce their carbon footprint and energy costs by adopting renewable energy practices such as installing solar panels, purchasing renewable energy credits, and implementing energy efficiency measures.
Investing in Renewable Energy Initiatives
Individuals can support renewable energy initiatives by investing in renewable energy funds, participating in community solar programs, and advocating for clean energy policies at the local, state, and national levels.
Conclusion
Renewable resource utilization holds immense potential to address climate change, promote economic development, and enhance energy security. By harnessing the power of renewable resources, we can create a more sustainable and resilient energy future for generations to come.
FAQs
- What are renewable resources? Renewable resources are natural energy sources that are replenished naturally over time, such as solar energy, wind power, hydroelectricity, biomass, and geothermal energy.
- What are the advantages of utilizing renewable resources? The advantages of utilizing renewable resources include environmental benefits, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, economic benefits, such as job creation and energy cost savings, and social benefits, such as improving public health and energy access.
- What are the challenges in utilizing renewable resources? Challenges in utilizing renewable resources include intermittency, storage issues, infrastructure requirements, and initial investment costs.
- How can governments promote renewable resource utilization? Governments can promote renewable resource utilization through subsidies, tax incentives, renewable energy targets, and supportive policies that create a favorable environment for investment and innovation.
- What is the future outlook for renewable resource utilization? The future outlook for renewable resource utilization is promising, with continued growth, innovation, and market opportunities expected to drive the transition to a sustainable energy future.


